1. Insertional Achilles Tendinosis
2. Haglund's deformity
3. Planter Fasciitis
4. Other cause of heel pain
1. Flat foot/Pes planus
2. High Arched foot/Cavus foot/ Pes cavus
3. Mid foot Arthritis
4. Stress fracture
5. Planter fibromatosis
6. Deformity of Foot Arch
7. Accessory Navicular
1. Hallux valgus/Bunion
2. Hallux rigidus
3. Hallux varus
4. ingrowing toenail
5. Painfull sesamoids
6. Arthritis around Great Toe
1. Complex deformities- cross over toe, Rheumatoid foot
2. Athlets feet
3. Corn's & Callosities
4. Morton's Neuroma
5. Metatersalgia
OCD of Talus
OCD or osteochondral lesion of talus is a condition that affects cartilage and its underlying bone at inner and outer corner of talar dome. It is a cartilage lesion where a patch of cartilage become soft or detached from underlying bone along with damage of the underlying bone. All this happens due to poor circulation of that cartilage patch. Medial side affects more than lateral side and most of the time medial lesion is not associated with any acute trauma. Nearly 70% of ankle fracture and sprain are associated with some form of OCD that may be symptomatic or asymptomatic.
OCD can happen at any age and usually associated with a history of ankle sprain or fracture. A patch of cartilage flap gets detached from underlying bone following ankle injury which become avascular and develops OCD. OCD can also happen due to chronic repetitive microtrauma which create ischemic environment over a patch of cartilage and its underlying bone and thus OCD develops.
Clinical symptom represents dull pain, swelling and stiffness of ankle during walking and sports activity. May have mechanical symptom like catching or locking. Initially it mimics an ankle sprain. There is no specific clinical finding related to talus OCD. It can remain asymptomatic for long and detect incidentally when x-ray is done for some other reason. This asymptomatic lesion can become symptomatic following an ankle injury.
If you feel the above mentioned symptom or your ankle pain does not subsides following few months after injury, should visit an specialist Foot & Ankle surgeon.
Your doctor will ask you regarding the nature and severity of pain and associated symptom. He may enquire about any old ankle injury. He will examine your ankle to elicit any tenderness over talus upper surface, ankle instability. There is no specific symptom or sign specific to OCD.
Basic imaging test is an ankle x-ray. In a non-conclusive x-ray finding MRI or CT scan is mandatory. MRI helps in diagnosis as well as the extent of the condition and planning of treatment. It also helps to rule out other cause of pain.
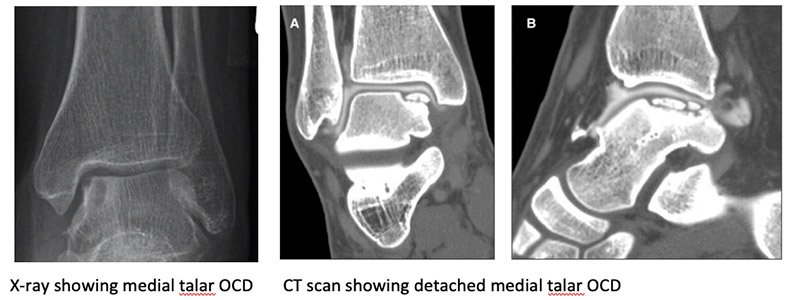

Treatment depends on severity of symptoms as well as preference of patient. Conservative treatment is recommended for early stages when the cartilage cap over the lesion is intact. And surgical treatment is recommended if the cartilage cap is detached or in non-responding cases with bony cyst underneath the cartilage.
Conservative treatment consist of:- NSAIDs and ICE pack to reduce pain
- Braces to stabilise ankle joint
- Physical therapy to strengthen ankle muscles and improve proprioception and range of movement.
Surgical treatment options are mainly arthroscopic but may require open surgery. Aim of the surgery is to remove the unstable cartilage which is the source of pain and stimulate healing
- Arthroscopic debridement and microfracture
- Open osteochondral grafting harvested from knee
- Reconstruction of associated ankle instability

