1. Insertional Achilles Tendinosis
2. Haglund's deformity
3. Planter Fasciitis
4. Other cause of heel pain
1. Flat foot/Pes planus
2. High Arched foot/Cavus foot/ Pes cavus
3. Mid foot Arthritis
4. Stress fracture
5. Planter fibromatosis
6. Deformity of Foot Arch
7. Accessory Navicular
1. Hallux valgus/Bunion
2. Hallux rigidus
3. Hallux varus
4. ingrowing toenail
5. Painfull sesamoids
6. Arthritis around Great Toe
1. Complex deformities- cross over toe, Rheumatoid foot
2. Athlets feet
3. Corn's & Callosities
4. Morton's Neuroma
5. Metatersalgia
Planter Fasciitis
Planter fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It happens due to accumulation microtrauma of planter fascia at its attachment with heel bone. Planter fascia is a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of foot and connects heel bone to toes. In most of the cases of planter fasciitis heel spur can be seen in x-ray. Earlier it was thought to be the causative factor of the pain in plater fasciitis which is not true. Its not the cause of pain rather it develops as a protective effort.
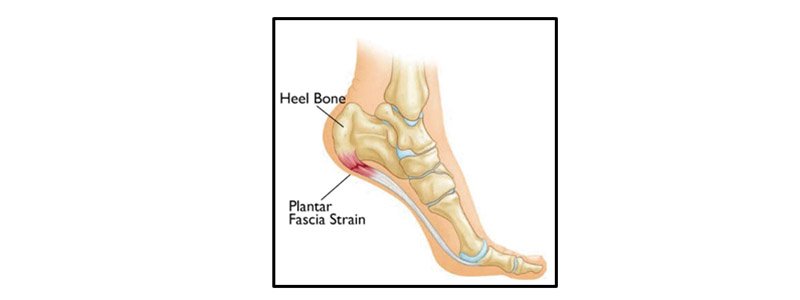
Plantar fasciitis is more common in runners, female, obese and in between age 40 to 60. Followings are the possible risk factor for developing planter fasciitis.
- Loss of ankle dorsiflexion due to tight gastrocnemius
- Pes cavus or pes planus deformities
- Excessive foot pronation
- Impact/weight bearing activities such as prolonged standing, running, exercising on hard surface, starting a new activity or sudden increase of the activity
- Improper shoe fit, high heel or worn out shoe
- Diabetes Mellitus or other metabolic conditions
- Heel pain with first steps in the morning or after long periods of non-weight bearing
- Tenderness to the anterior medial heel
- A limping gait or toe walking
- Pain is usually worse when walking barefoot on hard surfaces and with stair climbing
If you are having pain at bottom of heel which is continued for few weeks and causing significant disability you should visit a Foot & Ankle specialist
Your doctor will examine and palpate your heel for exact location of tender point. Also examine your foot and leg to find any predisposing factors like foot deformity and tight muscle. He may enquire about your daily activity, exercise and foot wear. Diagnosis is based on clinical judgment but your doctor may advice you an x-ray or MRI to exclude other cause of pain.
Mainstay of treatment is conservative based on physical rehabilitation. And most of the time it resolves with few weeks or months conservative treatment. Conservative treatment consist of
- Offloading and weight distribution at heel with silicon heel pad or soft insole
- Physiotherapy and exercise aiming to stretching gastrocnemius muscle and plantar fascia along with mobilisation and manipulation of Joint, gait training and balance training
- Night splints
- Analgesic and cold pack are recommended to alleviate acute painful condition.
Non responsiveness to conservative treatment for few months may render elevation of treatment modalities. These are minimal intervention to a surgical procedure
- Local infiltration at tender area with PRP
- Percutaneous release of planter fascia
- Dry needling
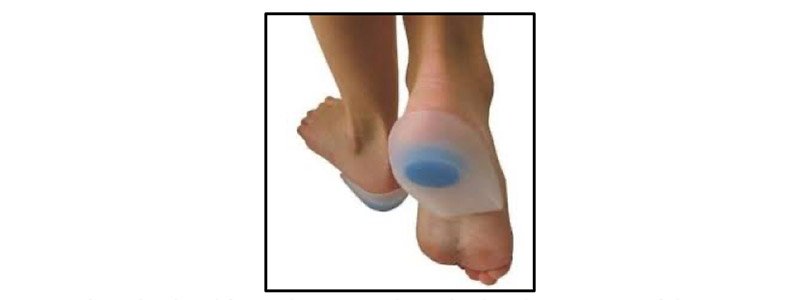
Silicon heel pad for cushioning and weight distribution at painful area Following relief from fasciitis one should continue stretching exercise of calf and sole, modify exercise and activity that was triggering the pain and use proper footwear can help them to avoiding.
